Building a MCP Client in Google Apps Script
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that allows AI assistants and tools to interact securely. While there are official SDKs for Node.js and Python, you might sometimes need a lightweight connection from a Google Workspace environment.
In this post, we’ll build a minimal MCP client using Google Apps Script’s UrlFetchApp.
Understanding the Protocol
MCP uses JSON-RPC 2.0 for communication. A typical session lifecycle involves:
- Initialization: Handshake to exchange capabilities.
- Tool Discovery: Listing available tools.
- Tool Execution: Calling specific tools to perform actions.
This implementation assumes you have an MCP server exposed via HTTP. I’m using the Google Workspace Developer Tools MCP Server for this example, https://workspace-developer.goog/mcp.
The Code
Here is the McpClient class that handles the handshake and method calls.
/**
* A simple MCP Client for Google Apps Script.
* Uses UrlFetchApp to communicate via JSON-RPC 2.0.
*/
class McpClient {
constructor(url) {
this.url = url;
this.sessionId = null;
this.requestId = 1;
}
/**
* Initializes the session and captures the session ID.
*/
initialize() {
const response = this.sendRequest("initialize", {
protocolVersion: "2024-11-05",
capabilities: {
roots: { listChanged: false },
sampling: {},
},
clientInfo: {
name: "AppsScriptClient",
version: "1.0.0",
},
});
this.sendNotification("notifications/initialized");
return response;
}
/**
* Lists available tools.
*/
listTools() {
return this.sendRequest("tools/list", {});
}
/**
* Calls a specific tool.
* @param {string} name
* @param {Object} args
*/
callTool(name, args) {
return this.sendRequest("tools/call", {
name: name,
arguments: args || {},
});
}
/**
* Closes the session.
*/
close() {
if (!this.sessionId) return;
const options = {
method: "delete",
headers: {
"MCP-Session-Id": this.sessionId,
},
muteHttpExceptions: true,
};
UrlFetchApp.fetch(this.url, options);
this.sessionId = null;
}
/**
* Sends a JSON-RPC request.
*/
sendRequest(method, params) {
const payload = {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: String(this.requestId++),
method: method,
};
if (params !== undefined) {
payload.params = params;
}
const options = {
method: "post",
contentType: "application/json",
headers: this._getHeaders(),
payload: JSON.stringify(payload),
muteHttpExceptions: true,
};
const response = UrlFetchApp.fetch(this.url, options);
// Capture session ID from initialization response if not already set
if (!this.sessionId && method === "initialize") {
const respHeaders = response.getHeaders();
// Headers might be case-insensitive or not, check both standard casing
this.sessionId =
respHeaders["MCP-Session-Id"] || respHeaders["mcp-session-id"];
}
const contentType = response.getHeaders()["Content-Type"] || "";
let json;
if (contentType.includes("text/event-stream")) {
const content = response.getContentText();
const lines = content.split("\n");
for (const line of lines) {
if (line.startsWith("data: ")) {
try {
const data = JSON.parse(line.substring(6));
if (
data.id === payload.id ||
data.result !== undefined ||
data.error !== undefined
) {
json = data;
break;
}
} catch (e) {
// ignore parse errors for keep-alive or malformed lines
}
}
}
if (!json) {
throw new Error("No valid JSON-RPC response in event stream");
}
} else {
json = JSON.parse(response.getContentText());
}
if (json.error) {
throw new Error(`MCP Error ${json.error.code}: ${json.error.message}`);
}
return json.result;
}
/**
* Sends a JSON-RPC notification (no id, no response expected).
*/
sendNotification(method, params) {
const payload = {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
method: method,
params: params,
};
const options = {
method: "post",
contentType: "application/json",
headers: this._getHeaders(),
payload: JSON.stringify(payload),
muteHttpExceptions: true,
};
UrlFetchApp.fetch(this.url, options);
}
/**
* Helper to construct headers.
*/
_getHeaders() {
const headers = {
Accept: "application/json, text/event-stream",
"MCP-Protocol-Version": "2024-11-05",
};
if (this.sessionId) {
headers["MCP-Session-Id"] = this.sessionId;
}
return headers;
}
}
And here is how you can use it:
/**
* A simple MCP Client for Google Apps Script.
* Uses UrlFetchApp to communicate via JSON-RPC 2.0.
*/
function runMcpClientDemo() {
// Replace with your MCP server URL
const SERVER_URL = "https://workspace-developer.goog/mcp";
const client = new McpClient(SERVER_URL);
// 1. Initialize
console.log("Initializing...");
const initResult = client.initialize();
console.log("Capabilities:", JSON.stringify(initResult, null, 2));
// 2. List Tools
console.log("Listing Tools...");
const tools = client.listTools();
console.log("Available Tools:", JSON.stringify(tools, null, 2));
// 3. Call Tool
if (tools.tools && tools.tools.length > 0) {
const toolName = tools.tools[0].name;
const result = client.callTool(toolName, { query: "Apps Script" });
console.log("Result:", JSON.stringify(result, null, 2));
}
// 4. Close Session
console.log("Closing session...");
client.close();
}
1. Initialization (Handshake)
The session starts with an initialize request. The client sends its protocol version and capabilities. The server responds with its own.
9:59:38 AM Info Initializing...
9:59:38 AM Info Capabilities: {
"protocolVersion": "2024-11-05",
"capabilities": {
"experimental": {},
"prompts": {
"listChanged": false
},
"resources": {
"subscribe": false,
"listChanged": false
},
"tools": {
"listChanged": false
}
},
"serverInfo": {
"name": "Google Workspace Developers",
"version": "unknown"
},
"instructions": "First, use the search_workspace_docs tool..."
}2. Listing Tools
Once initialized, we can see what the server offers using tools/list.
9:59:38 AM Info Available Tools: {
"tools": [
{
"name": "search_workspace_docs",
"title": "Search Google Workspace Documentation",
"description": "Searches the latest official Google Workspace doc...",
"inputSchema": {
"properties": {
"query": {
"description": "The query to search.",
"maxLength": 100,
"minLength": 5,
"title": "Query",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"query"
],
"title": "search_toolArguments",
"type": "object"
},
"outputSchema": {
"$defs": {
"SearchResult": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"description": "The title of the search result.",
"title": "Title",
"type": "string"
},
"url": {
"description": "The URL of the search result.",
"title": "Url",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"title",
"url"
],
"title": "SearchResult",
"type": "object"
}
},
"properties": {
"results": {
"description": "The search results.",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/SearchResult"
},
"title": "Results",
"type": "array"
},
"summary": {
"description": "The summary of the search results.",
"title": "Summary",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"results",
"summary"
],
"title": "SearchResponse",
"type": "object"
},
"annotations": {
"readOnlyHint": true,
"destructiveHint": false,
"idempotentHint": true,
"openWorldHint": true
}
},3. Calling Tools
To use a capability, we send a tools/call request with the tool name and arguments.
const toolName = tools.tools[0].name;
const result = client.callTool(toolName, { query: "Apps Script" });
console.log("Result:", JSON.stringify(result, null, 2));And the result looks like this:
10:03:47 AM Info Result: {
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "{\n "results": [\n {\n ..."
}
],
"structuredContent": {
"results": [
{
"title": "Google Apps Script overview",
"url": "https://developers.google.com/apps-script/overview"
},
// ...OMITTED
{
"title": "Manifests",
"url": "https://developers.google.com/apps-script/concepts/manifests"
}
],
"summary": "Apps Script enhances Google Workspace. It adds..."
},
"isError": false
}Integrating with Vertex AI
One of the most powerful uses of MCP is giving LLMs access to your tools. Since MCP uses JSON Schema for tool definitions, we can easily adapt them for Vertex AI function calling.
/**
* Demonstrates using MCP tools with Vertex AI.
*/
function runVertexAiAgent() {
const SERVER_URL = "https://workspace-developer.goog/mcp";
const PROJECT_ID = "YOUR_PROJECT_ID";
const LOCATION = "global";
const MODEL_ID = "gemini-3-flash-preview";
const client = new McpClient(SERVER_URL);
client.initialize();
// 1. Adapt MCP tools for Vertex AI
const tools = client.listTools();
const functionDeclarations = tools.tools.slice(0, 1).map((tool) => ({
name: tool.name,
description: tool.description,
parameters: tool.inputSchema,
}));
// 2. Call the Model using Vertex AI Advanced Service
const model =
`projects/${PROJECT_ID}/locations/${LOCATION}` +
`/publishers/google/models/${MODEL_ID}`;
const payload = {
contents: [
{
role: "user",
parts: [
{
text: "How do I call Gemini from Apps Script in two sentences.",
},
],
},
],
tools: [{ functionDeclarations }],
// Model is constrained to always predicting function calls only.
toolConfig: { functionCallingConfig: { mode: "ANY" } },
};
const url = `https://aiplatform.googleapis.com/v1/${model}:generateContent`;
const options = {
method: "post",
contentType: "application/json",
headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${ScriptApp.getOAuthToken()}` },
payload: JSON.stringify(payload),
muteHttpExceptions: true,
};
const response = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
const json = JSON.parse(response.getContentText());
const content = json.candidates[0].content;
const part = content.parts[0];
// 3. Execute Tool Call
if (part.functionCall) {
const fn = part.functionCall;
console.log(fn);
const result = client.callTool(fn.name, fn.args);
// 4. Call the Model again with the tool result
payload.contents.push(content);
payload.contents.push({
role: "function",
parts: [
{
functionResponse: {
name: fn.name,
response: { name: fn.name, content: result },
},
},
],
});
console.log("Payload now contains tool result");
console.log(payload.contents);
// Remove tools
delete payload.tools;
options.payload = JSON.stringify(payload);
const response2 = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
const answer = JSON.parse(response2.getContentText()).candidates[0].content
.parts[0].text;
console.log(answer);
}
// 5. Use it in a loop for agentic behavior
// TODO(developer): Implement agent loop
}
OAuth Scopes
To use Vertex AI, you must explicitly add the cloud-platform scope to your appsscript.json. If you use UrlFetchApp, you also need script.external_request.
{
"timeZone": "America/Denver",
"dependencies": {},
"exceptionLogging": "STACKDRIVER",
"runtimeVersion": "V8",
"oauthScopes": [
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform",
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/script.external_request"
]
}
Apps Script recently released a built-in Vertex AI Advanced Service. You can use that instead of UrlFetchApp for a cleaner experience, but the REST API approach shown above works everywhere.
Vertex AI MCP Tool Calling
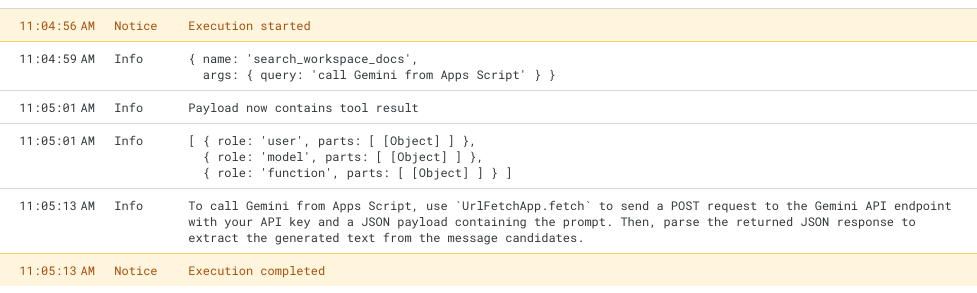
Here is what the code looks like to call the MCP server from Vertex AI in Apps Script.
- The initial Vertex AI call contains the tool definitions from the MCP
tools/listcall. - The model then returns the function calls and params.
- Another Vertex AI call is made with the tool result(now without allowing tools).
- Gemini via the Vertex AI summarizes the content (
user,model,tool) into another output.
Summary
This simple wrapper allows Google Apps Script to act as an MCP Client, enabling you to integrate your Workspace automation directly with the growing ecosystem of MCP servers.
Further Reading
- MCPApp: A MCP client/server library for Apps Script by Kanshi Tanaike.
- Connect Gemini to Google Apps Script via MCP: A guide on building an MCP Server in Apps Script.
- Vertex AI Advanced Service: The Vertex AI Advanced Service for Apps Script.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use
stdioorsseMCP servers?No.
stdiodoesn't work because Apps Script is in the cloud andsseor HTTP Server Sent Events are not supported in Apps ScriptUrlFetchApp.How do I authenticate the MCP server?
You should use servers that support key-based or long lived tokens in headers. Google MCP servers might support the Apps Script OAuth token if you have the correct scopes defined! See Secure Secrets in Apps Script.
Can I use this to connect to Google APIs like Drive or Gmail?
Maybe. This client is for communicating with an MCP server. However, you could build an MCP server that exposes tools for interacting with Google APIs. For example, your MCP server could have a
createDoctool that uses the Google Drive API. This client would then call your MCP server'screateDoctool. If you don't have this server already, it is probably easier to just create the Apps Script method/tool directly.
Opinions expressed are my own and do not necessarily represent those of Google.
© 2026 by Justin Poehnelt is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0